|
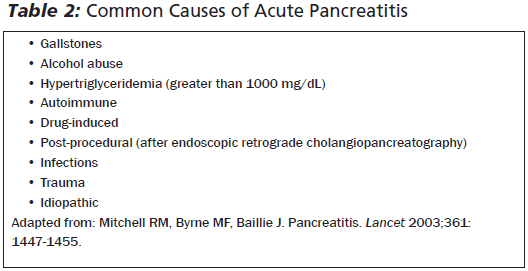
Adapted from Katie Januszewicz's Grand Rounds lecture August 30th, 2017 Inflammation of the pancreas can be limited to mild inflammation to severe necrosis of the pancreas and surrounding tissue. Most cases (80%) involve only mild inflammation, however severe pancreatitis can lead to a 30% mortality rate. Most cases are secondary to gallstones or alcohol, but up to 5% of ERCP patients present with post-procedure pancreatitis. Additionally, many medications (120) can cause pancreatitis. In severe cases this can lead to inflammatory responses in nearby tissue and even systemically.
Pancreatitis occurs secondary to an unclear mechanism involving trypsin, a protease that is typically converted from pancreatic trypsinogen in the duodenum. When trypsin is activated in the pancreatic acinar cells, this continues unregulated leading to activation of other digestive enzymes and auto-digestion of the pancreas.
0 Comments
Pulmonary embolisms present with a broad variety of symptoms from chest pain to shortness of breath, and even fevers. Common exam findings include tachypnea and tachycardia. Risk factors include recent surgery, trauma, prolonged immobility, active cancer, birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy, or a history of prior embolism. Definitions
Pulmonary Embolism is the Arresting PatientPatients who arrest with a strong suspicion of pulmonary embolism may be treated with TPA. Bedside ultrasound should be used to help rule out alternative causes, such as tamponade or aortic dissection. Bedside ultrasound should also be used to evaluate for right heart strain prior to TPA.
The initial dose of TPA in a cardiac arrest varies depending on what study is being evaluated. Some doses include an initial bolus of 10-15mg of TPA followed by an influsion of 85-90mg over an hour. Local protocol calls for a single bolus of 50mg over 2 minutes in cardiac arrest. This should be followed by at least 15-20 additional minutes of CPR to allow for TPA to circulate. A second dose could be considered. Current data shows that there is no difference in outcome when comparing patients who do and do not receive TPA during cardiac arrest. The same data also does not show increased risk of severe bleeding when comparing these populations. Undifferentiated cardiac arrest is NOT an indication for TPA. Adapted from Dr. Brian D’Cruz’s Grand Round Lecture August 23, 2017 In addition to classical GI complaints such as giardia, tropical areas have the additional issues such as limited resources, lack of physicians, and potentially poorly treated water resources. Severe malnutrition and dehydration are common complaints.
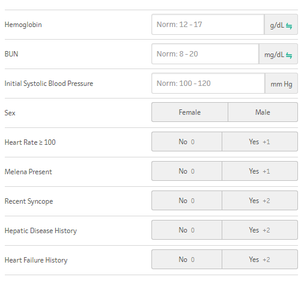
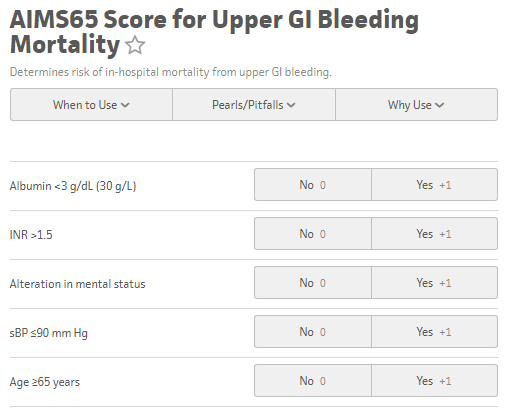
The GBS score can be utilized for upper GI bleeds to risk stratify patients for potential discharge from the emergency department, and was originally published in 2000 in the Lancet based off a Scottish study in 1997 and validated in 2007. The GBS classifies Low Risk as those patients with a score of Zero. Any score higher than zero is considered to potentially require intervention, transfusion, or endoscopy The AIM65 Score is a less complicated scoring system derived retrospectively in 2011 from a cohort of >29,000 patients.
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors include carbamates, organophosphates, and chemical weapons, which bind to carboxylic esters, such as acetylcholinesterase at the nerve terminals and within RBCs. These are commonly used as pesticides, but have also been utilized as chemical weapons, such as the Tokyo subway poisoning in 1995 which utilized Sarin.
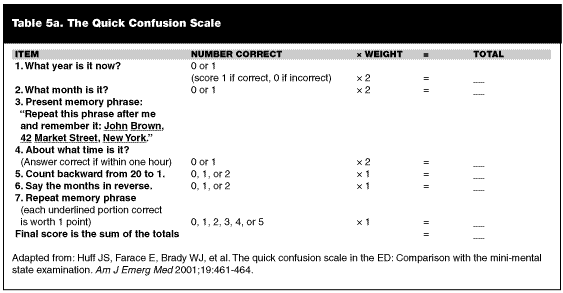
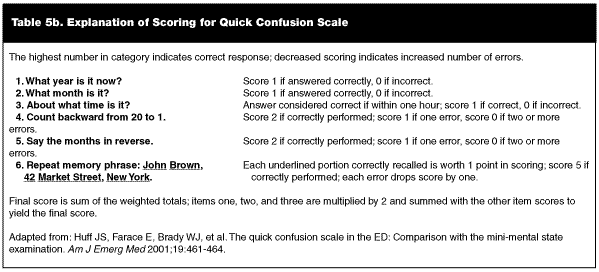
Additionally, many Alzheimer medications are also acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, and can give the same symptoms when at elevated amounts or overdose, and can present with vague or mild symptoms. The QCS can be administered more quickly than the MMSE, and is easier to administer in the ED
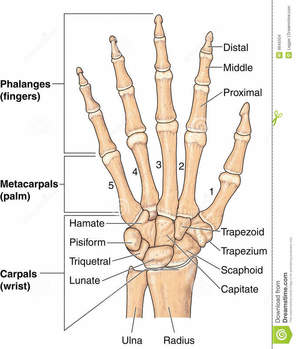
Wrists are the most commonly injured upper extremity joint, and 8.8% of injuries are missed, with 2% being clinically important. With 27 bones and 34 muscles, there is a significant possibility of missing a fracture. A high index of suspicion is required to prevent missing a significant injury.
|
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|
||||||||