|
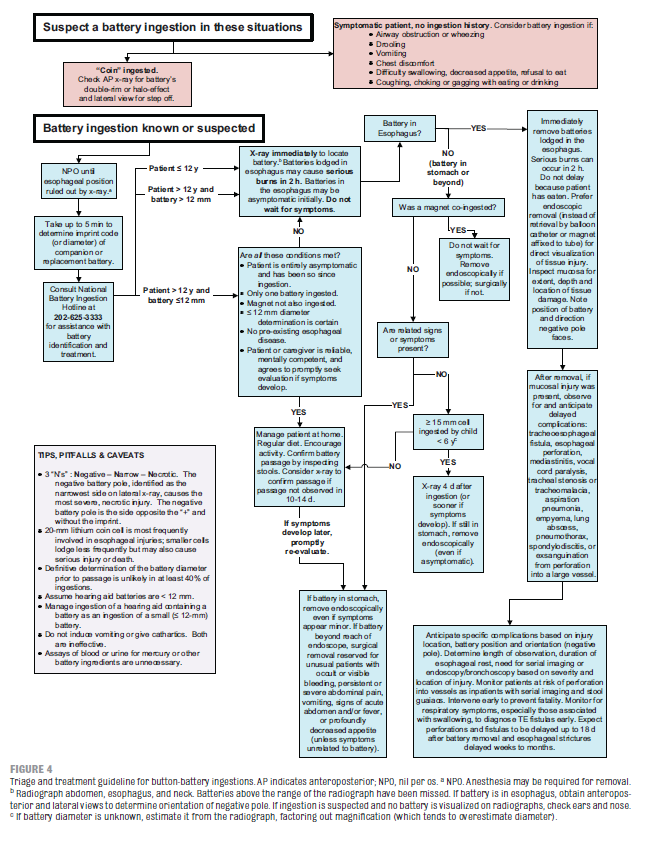
According to an article published by the American Academy of Pediatrics in 2010, severe and fatal battery ingestions are increasing, and many patients are being treated inadequately for button battery ingestions. From 1985 to 1009, there has been a 6-fold increase in button battery ingestions with resulting major or fatal outcomes. The largest increase has been with lithium-cell batteries (24% of ingestions) and 20-25mm diameter batteries (18% of ingestions). 20mm lithium cells are the most common to be associated with severe outcomes.
A high index of suspicion is needed; 54% of fatal outcomes are misdiagnosed, usually complicated by nonspecific presentations. Most serious battery ingestions are not witnessed. Consider an ingestion anytime a patient is wheezing, drooling, vomiting, or has chest pain or discomfort.
0 Comments
Adapted from CPC presentation by Molly Graham, November 11th, 2016 Differential Diagnosis for joint pain in a pediatric patient
HSP is the most common systemic vasculitis seen in children, and is characterized by palpable purpura without thrombocytopenia or coagulopathy, as well as abdominal pain, joint pains, proteinuria or hematuria. To diagnose HSP, a patient must have palpable purpura with a predominance of the lower extremities, and one additional symptom or finding on physical exam. Diffuse abdominal pain is commonly the first symptom and may include the testicles in males, but other gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting may be the first sign of disease, followed by skin findings. Patients with severe abdominal pain should be evaluated with an abdominal ultrasound to evaluate for intussuception or peritoneal fluid.
HSP symptoms are due to IgA deposits, while the trigger is still unknown, These deposits may be associated with a recent URI, group A strep infection, cold weather, or insect bites. Glomerular inflammation is typically self-limited, but in rare cases can lead to life-long renal disease. Additional complications of HSP include neurologic symptoms (headaches, seizures) and intussusception secondary to intestinal wall inflammation. Most patients (90%) are under the age of 17, and present in the fall or winter. Diagnosis of HSP is typically clinical, however a skin biopsy of a lesion can be taken to identify leukocytoclastic vasculitis. Treatment includes NSAIDs for pain control, Before every lumbar puncture many providers reactively get a CT to rule out a mass or reduce the risk of herniation, However, not every patient requires a CT.
Neonates (<28 days of age) are a fragile population that can present in life-threatening distress that requires immediate evaluation and treatment. As such, utilizing a systematic approach can help identify and treat the most common causes of neonatal distress. As more hospital nurseries discharge patients earlier, emergency departments must be ready to evaluate, diagnose, and treat neonatal emergencies. For more information; ACEP "The Misfits" The MisfitsThe Misfits is a useful mnemonic for neurologic changes in the neonate, and can be expanded to neonatal distress in general to aid in a systematic approach to all neonates in distress. Keep in mind that neurologic changes in the very young may be subtle and difficult to diagnose.
Intestinal Emergencies |
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|