|
Especially in the summer, children, and young men are at higher risk of submersion injuries. Management of a drowning victimWhen a patient is identified in an active drowning situation;
0 Comments
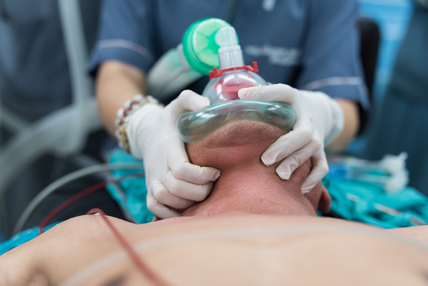
Adapted from Will Denq's Grand Rounds presentation August 24th, 2016 A discussion of preoxygenation as well as the role of high flow nasal cannula and apneic oxygenation in the emergency setting.
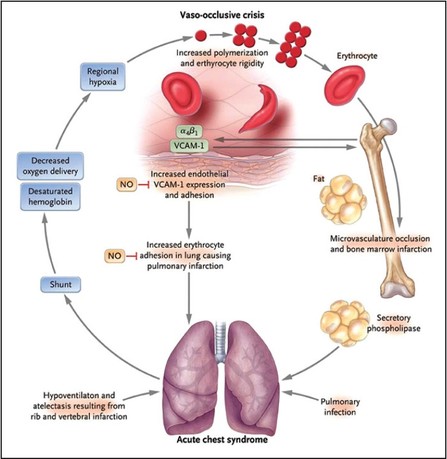
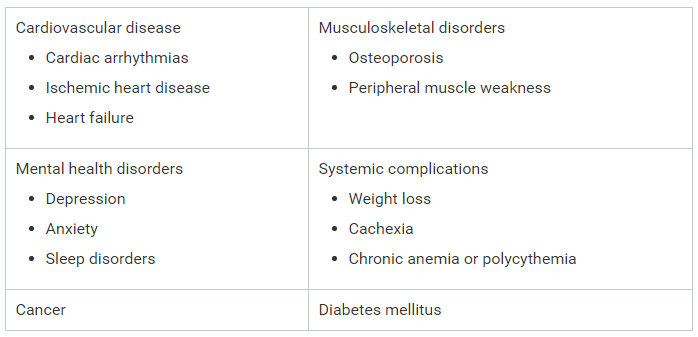
Adapted from Colton Hood's August 17th 2016 Grand Rounds lecture. One of the most common and severe complications of sickle cell disease, clinically may resemble a pneumonia, and can develop suddenly, and is more common in patients with asthma or those with prior acute chest events. Typically presents with cough, shortness of breath, and rales accompanied by a new infiltrate on chest X-ray. Mortality of acute chest syndrome is 9% in adults, and can lead to pulmonary hypertension, right heart failure, and risk of sudden death. Evaluate patients with sickle cell disease with acute onset of lower respiratory tract disease with or without fever for acute chest syndrome, including chest x-ray and pulse oximetry to measure oxygen saturation (NHLBI Consensus-Panel Expertise) Appropriate Syncope Workup
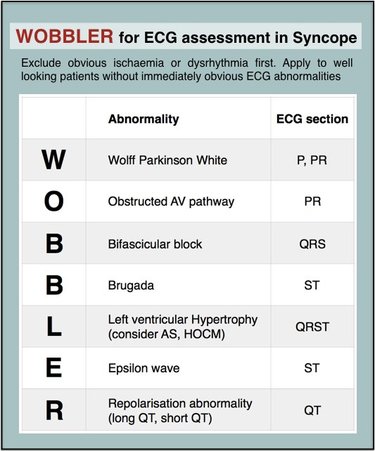
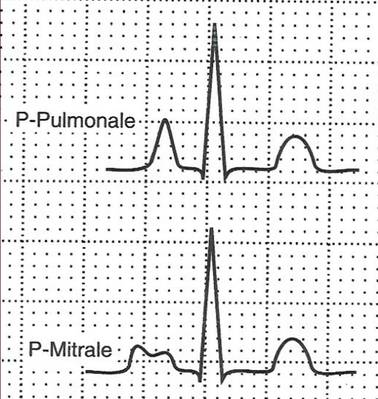
EKG Abnormalities in Syncope
Disposition of Syncopal Patients ACEP Risk Factors in Syncope ACEP Risk Factors in Syncope
Adapted from Molly Graham's August 17th 2016 Grand Rounds presentation. Treatment of acute COPD exacerbationAcute exacerbations are characterized by sustained (48 hours or more) worsening of shortness of breath and coughing, with or without sputum. The most common cause is a viral or bacterial infection.
Risk Factors
Procalcitonin LevelsPeptide inflammatory marker currently being evaluated for use as a POC marker for inflammatory and infectious disease. Evaluation of COPD exacerbations with procalcitonin can decrease antibiotic use. A PCT <0.1ng/mL indicates patient outcomes will not be improved with antibiotics.
Before every lumbar puncture many providers reactively get a CT to rule out a mass or reduce the risk of herniation, However, not every patient requires a CT.
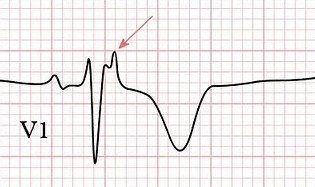
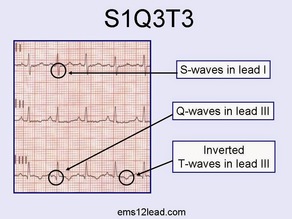 Case: 22F cc: chest pain, dyspnea Dx: Pulmonary embolism EKG changes in PE:
|
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|
||||||||||||||||||