Appropriate Syncope Workup
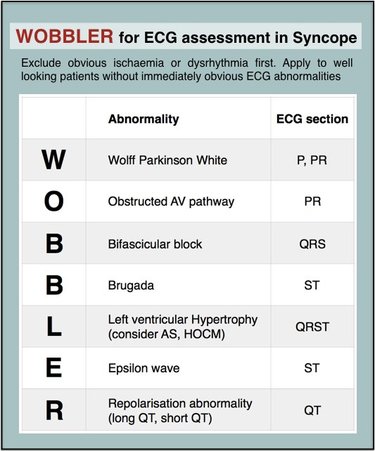
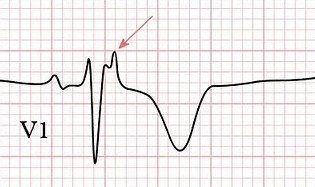
EKG Abnormalities in Syncope
Disposition of Syncopal Patients ACEP Risk Factors in Syncope ACEP Risk Factors in Syncope
0 Comments
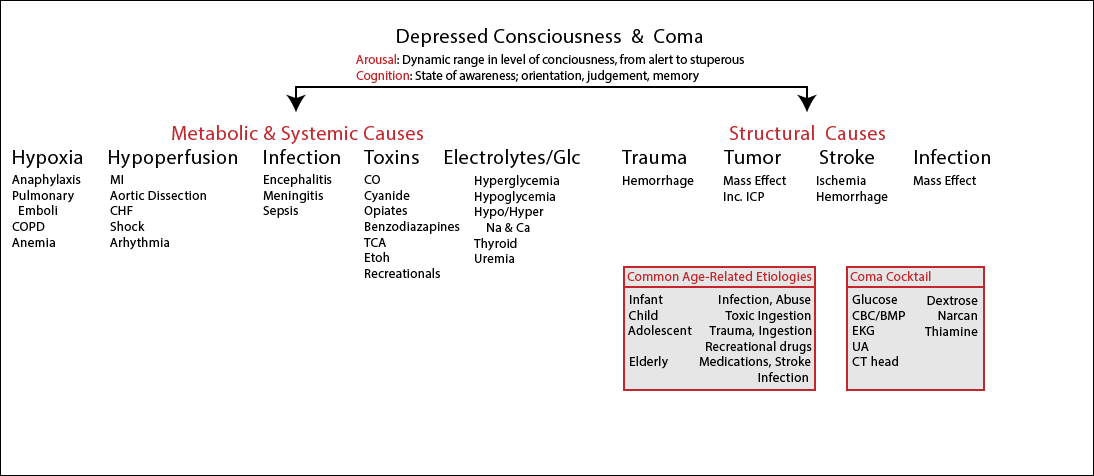
Adapted from Rosens, chp 16. Little Old Lady Workup (LOL)Testing to consider in an elderly patient with altered mental status ABG: hypoxia, CO2 retention, SOB BMP/CMP: electrolyte abnormalities, hepatic encephalopathy UA: infection, DKA, ingestion PT/INT: hemorrhage, anemia, hypercoagulable Lactate: ketotic state, ingestion, ischemia TSH: thyroid storm, hypothyroid Cardiac Enzymes: MI, ischemia, cardiogenic shock CXR: infection, pneumothorax, CHF CT head: hemorrhage, mass MRI: edema, mass, ischemia CTA: pulmonary emboli, aortic dissection LP/CSF: infection, ICP Confusion
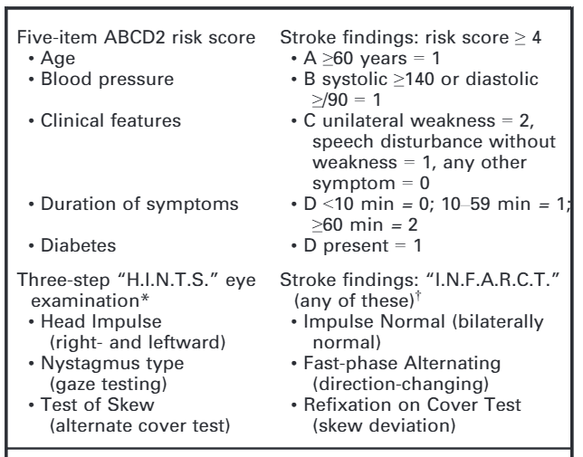
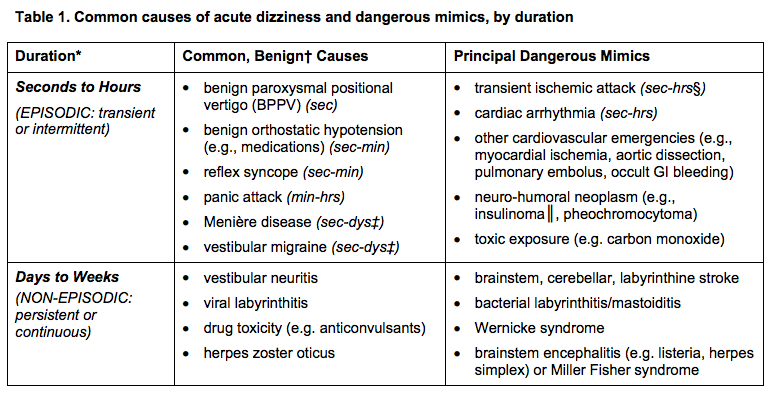
Adapted from a presentation by Ty Nichols, 12/2/2015 Dizziness can be difficult to assess in the ED given the vast range of etiologies and varying ways patients interpret their symptoms. Additionally, not all patients with emergency conditions will present with obvious focal deficits. A clinical decision making rule (HINTS) can help to more rapidly identify stroke patients to initiate acute therapies faster. The HINTS rule outperforms ABCD2 for stroke diagnosis in the ED when performed by qualified practitioners in patients with Acute Vestibular Syndrome. A mechanism to risk stratify patients presenting with syncope
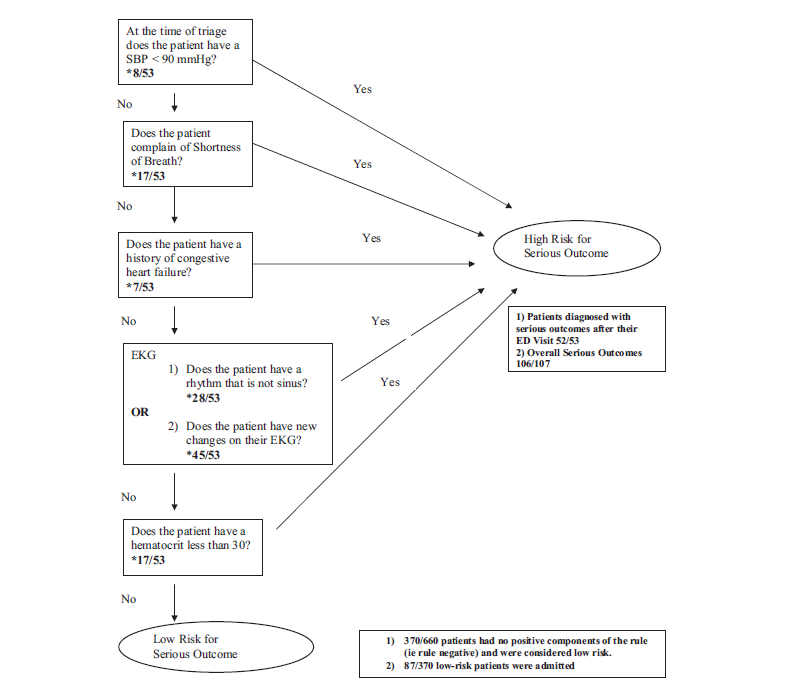
The SFSR is criticized as being unsafe given a high miss rate (pooled sensitivity of 86%). Notably, there is one patient in the original trial who was SFSR negative and subsequently died (cardiac arrest after inpatient hospital discharge). Exclusion Criteria
|
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|