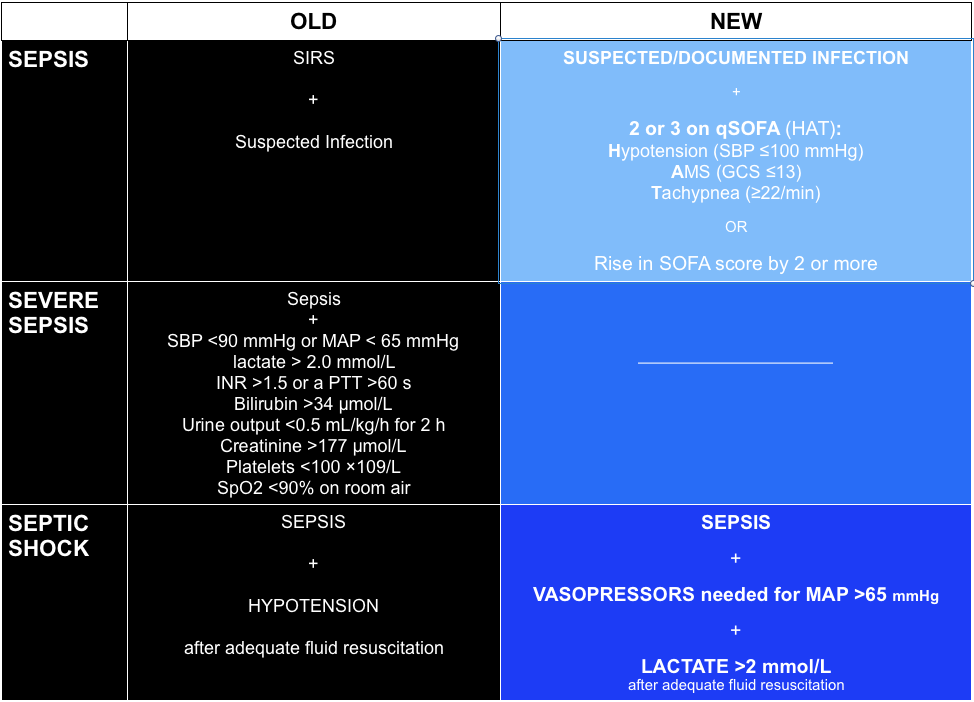
Current Definitions
Blood CulturesUtilization of blood cultures can assist the treatment of many patients, however not every patient requires blood cultures. Whenever drawn, you should obtain two sets of cultures (or 3 for endocarditis). A recent article found a number needed to treat was 250 for a change in treatment, however other studies have found blood cultures more useful. Major Criteria:
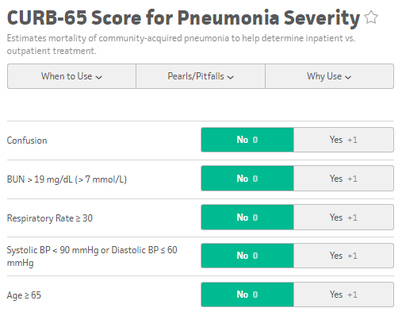
www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0736467908004447?via%3DihubA blood culture is indicated by the rule if at least one major criterion or two minor criteria are present. Admission Criteria: CURB 65 and PSI/PORTPatients with CURB 65 scores 0-1 can potentially be discharged, however consider the patient's physical exam, oxygen saturation, and immunosupressed status, as the CURB 65 score does not take these into account. Those with a CURB 65 score greater than 3 should be considered for an ICU admission. The PSI/PORT score can also be used but is more thorough, including nursing home status, liver and heart disease status, as well as ABG data. While the CURB 65 has better specificity for identifying severe disease, the PSI/PORT score is more sensitive at identifying low-risk patients for discharge. TreatmentFor CAP, guidelines recommend Azithromycin or Doxycycline as azythromycin has increasing rates of resistance. In outpatients with co-morbidities or risk for resistance, you should consider levofloxacin or moxifloxacin. Patients admitted for CAP should be treated with single agent fluoroquinolone or dual agent treatment with ceftriaxone and azithromycin. ICU admitted CAP patients require an anti-pneumococcal betalactam (Ceftriaxone) and either azithromycin or fluoroquinolone. Treatment duration is typically 5 days.
1 Comment
Adapted from Molly Graham's August 17th 2016 Grand Rounds presentation. Treatment of acute COPD exacerbationAcute exacerbations are characterized by sustained (48 hours or more) worsening of shortness of breath and coughing, with or without sputum. The most common cause is a viral or bacterial infection.
Risk Factors
Procalcitonin LevelsPeptide inflammatory marker currently being evaluated for use as a POC marker for inflammatory and infectious disease. Evaluation of COPD exacerbations with procalcitonin can decrease antibiotic use. A PCT <0.1ng/mL indicates patient outcomes will not be improved with antibiotics.
I. Urinalysis
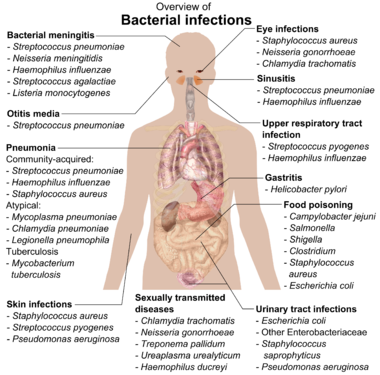
Most Common Pathogens
II. Spectrum of Disease |
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|
||||||||