|
Adapted from Katie Januszewicz's Grand Rounds lecture August 30th, 2017 Inflammation of the pancreas can be limited to mild inflammation to severe necrosis of the pancreas and surrounding tissue. Most cases (80%) involve only mild inflammation, however severe pancreatitis can lead to a 30% mortality rate. Most cases are secondary to gallstones or alcohol, but up to 5% of ERCP patients present with post-procedure pancreatitis. Additionally, many medications (120) can cause pancreatitis. In severe cases this can lead to inflammatory responses in nearby tissue and even systemically. Pancreatitis occurs secondary to an unclear mechanism involving trypsin, a protease that is typically converted from pancreatic trypsinogen in the duodenum. When trypsin is activated in the pancreatic acinar cells, this continues unregulated leading to activation of other digestive enzymes and auto-digestion of the pancreas. DiagnosisDiagnosis is based on at least two of three criteria;
ALT elevation > 150 U/L within the first 48 hours of symptoms has a 85% positive predictive value of gallstone pancreatitis. Reserve CT imaging for cases of diagnostic uncertainty, severe pancreatitis, especially if high suspicion of complications (pseudocyst, necrosis). Abdominal ultrasound can be helpful in confirming cases of gallstone pancreatitis, but is not the gold standard for pancreatitis imaging. There is no evidence that early CT improves clinical outcomes.
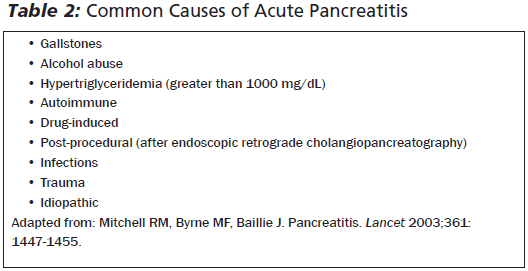
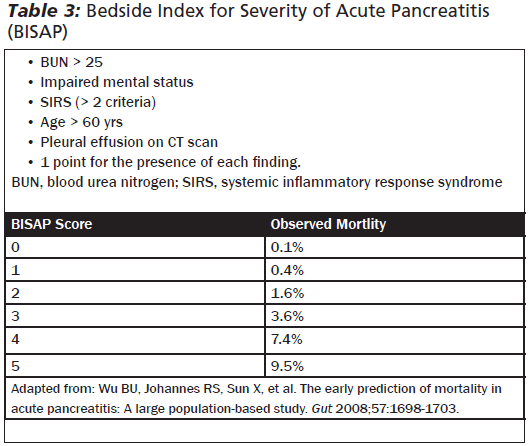
Management & DispositionMainstay of management is supportive care (analgesia, antiemetics, maintenance IV fluids). Diet should be NPO, unless the case is mild and the patient can tolerate PO. Prophylactic antibiotics are not recommended. Scoring systems can be helpful to determine mild to severe cases of pancreatitis. In the ED, it is easiest to obtain a BISAP score for mortality risk (as compared to a Ranson score which is becoming outdated). Disposition ranges from discharge (mild case, tolerating PO) to ICU admissions (hemodynamically unstable, severe pancreatitis, signs of end organ damage). The rest can be admitted to the floor and may require surgical consults (if planning cholecystectomy, etc.) or GI consults (for ERCP).
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|
||||||