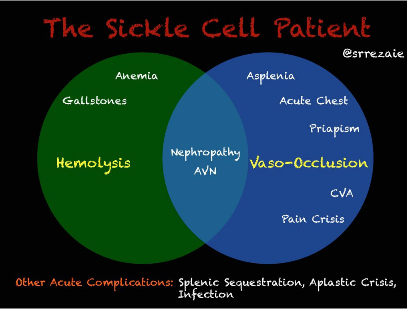
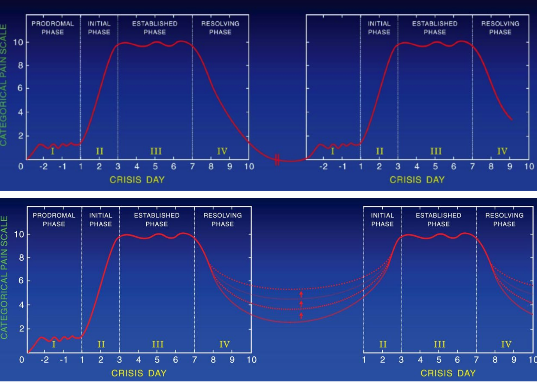
Sickle cell patients can present in both hemolysis (anemia, gallstones, nephropathy) and/or vaso-occlusive symptoms (acute chest, priapism, CVA, pain crisis). Sickle cell pain crisis can be caused by a broad range of triggers, and vary broadly between patients, including heat/cold, exercise, dehydration, infection, menses and other causes. Many episodes are thought to be spontaneous. Vitals signs can frequently be normal, despite the patient suffering severe pain crisis. The NIH gold standard for sickle cell pain assessment is the patient's report of pain, and no combination of lab or clinical findings exist to determine if the patient is indeed in pain. Additionally, as the patient ages, the amount of pain between crises increases. Evaluation of the sickle cell patient: Maintaining a high suspicion of additional medical illnesses is important. A WBC >20,000 is not typical for sickle cell.. When evaluating reticulocyte counts, <3% is indicative of an aplastic crisis, while >12% indicates rapid hemolysis. Additional labs to consider include LDH, biirubin and haptoglobin. Pain Management: Prompt administration and rapid reassessment. If pain is not relieved with >2 doses, hospitalization is recommended for analgesia.
Yawn, Barbara P., et al. "Management of sickle cell disease: summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by expert panel members." Jama 312.10 (2014): 1033-1048.
Ballas, S. K. "The Sickle Cell Painful Crisis in Adults: Phs and Objective Signs." Hemoglobin 19.6 (1995): 323-333. Raphael, Jean L., and Suzette O. Oyeku. "Sickle cell disease pain management and the medical home." ASH Education Program Book 2013.1 (2013): 433-438. Benjamin, Lennette J., Gwendolyn I. Swinson, and Ronald L. Nagel. "Sickle cell anemia day hospital: an approach for the management of uncomplicated painful crises." Blood 95.4 (2000): 1130-1136. Okomo, Uduak, and Martin M. Meremikwu. "Fluid replacement therapy for acute episodes of pain in people with sickle cell disease." The Cochrane database of systematic reviews 3 (2015). Bartolucci, Pablo, et al. "A randomized, controlled clinical trial of ketoprofen for sickle-cell disease vaso-occlusive crises in adults." Blood 114.18 (2009): 3742-3747.
2 Comments
<a href="https://jayhealthcare.com/product/cbd-isolate-powder/">where to buy CBD Isolate Powder online</a>
Reply
1/22/2024 07:46:23 pm
Thanks for sharing this informative blog with us:
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|