|
There are currently an estimated 11 million people in the world infected with TB, and there were 9,412 cases in the United States in 2014. The American Thoracic Society, Center for Disease Control and Prevention, and the Infectious Diseases Society of America have all come together to create a new guideline for diagnosing pulmonary, extrapulmonary, and latent tuberculosis in adults and children.
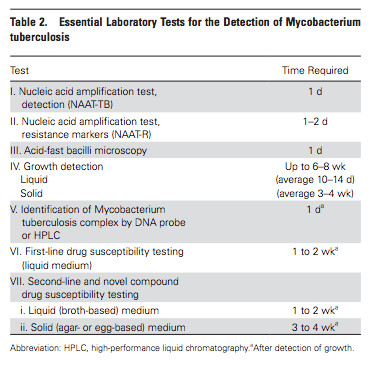
The recommendations include: • Acid-fast bacilli smear microscopy should be performed in all patients suspected of having pulmonary TB, using at least three sputum samples. A sputum volume of at least 3 mL is needed, but 5-10 mL would be better.• Both liquid and solid mycobacterial cultures should be performed on every specimen from patients suspected of having TB disease, rather than either type alone. • A diagnostic nucleic acid amplification test should be performed on the initial specimen from patients suspected of having pulmonary TB. • Rapid molecular drug susceptibility testing of respiratory specimens is advised for certain patients, with a focus on testing for rifampin susceptibility with or without isoniazid. • Patients suspected of having extrapulmonary TB also should have mycobacterial cultures performed on all specimens. • For all mycobacterial cultures that are positive for TB, a culture isolate should be submitted for genotyping to a regional genotyping laboratory. • For patients aged 5 and older who are suspected of having latent TB infection, an interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) is advised rather than a tuberculin skin test, especially if the patient is not likely to return to have the test result read. A tuberculin skin test is an acceptable alternative if IGRA is not available, is too expensive, or is too burdensome.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|
||||||||