|
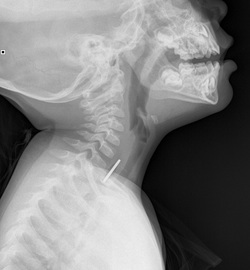
How to manage common presentations of esophageal foreign bodies in adults and children. Adapted from Ainsley Adams' Grand Rounds Lecture, September 7th, 2016. Most common locations for foreign bodies:
Food BolusEvaluate for trouble with secretions including drooling or trouble swallowing, and determine how long the foreign body sensation has been present. Identify any known esophageal or mediastinal masses, including hiatal hernias and any prior procedures. Evaluation includes visualization of the posterior pharynx with a laryngosope. Treatment options includes effervescent powders or soda, although this should not be attempted in those with pain or presentation concerning for esophageal rupture. Glucagon may be attempted, although only 1/3 of patients will have positive results, and glucagon can cause severe emesis.
If your patient continues to have a foreign body sensation yet X-ray is not identifying any foreign body, it is advisable to obtain CT imaging to prevent future complications including abscess formation and erosion into the mediastinum.
Batteries & BabiesWhen concerned for a battery ingestion, it is important to identify the location and type of battery. Button batteries specifically can rapidly cause liquefactive necrosis, burns and perforation. Early consultation is important to prevent continuing trauma and damage. Button Batteries: Esophageal batteries are surgical emergencies. If a battery progresses to the stomach, expected management can begin unless there is concern for poor follow up or that the battery may be too large to pass. Regular Batteries; Esophageal batteries are an emergency as well, however once it passes to the stomach can be managed expectantly. Coins: Non-obstructive FB should be admitted for tracking until it is determined the FB will pass. Single magnets can be managed similarly. Magnets; More than one magnet, or a magnet plus another metal object or battery are usually surgical emergencies. Food Boluses: Associated with eosinophilic esophagitis in children, and specialists should be involved early. Plastics: Treatment depends on the shape, size, and ability to pass.
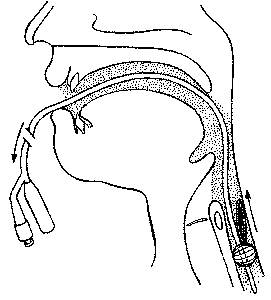
Emergency removal of foreign bodiesFoley catheter balloon extraction is an easily performed, relatively effective, and safe method of removing blunt foreign bodies from the esophagus. It avoids the morbidity and costs of endoscopy, general anesthesia, and hospitalization. The procedure is most appropriate for removing flat, two-dimensional foreign bodies, such as coins and discs, because the relatively large Foley catheter can slide easily beside and beyond these objects. The reported success rate for this procedure in more than 2500 patients is 95%. The incidence of complications is 0.4%. Only one death has been well documented and reported with this technique, and that was due to airway occlusion by a coin that was aspirated during its withdrawal.
Generally accepted contraindications to Foley catheter balloon extraction are the presence of:
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|
||||||||||||||||||