|
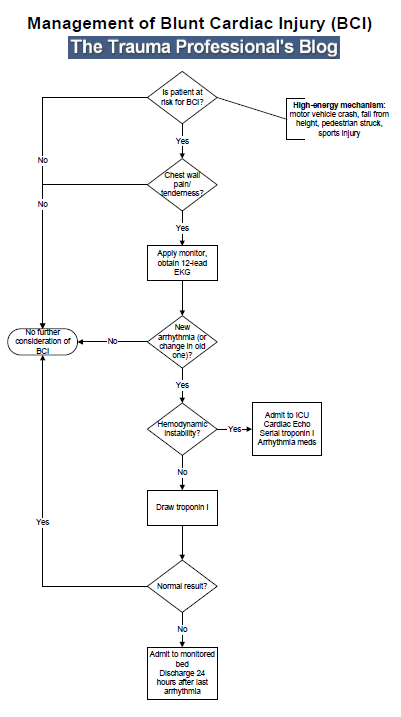
Adapted from Kristin Schreiber's Grand Rounds presentation, October 18th, 2016 Blunt Cardiac InjuryAny traumatic injury which effects the heart's ability to function. Normally diagnosed via EKG and blood monitoring. Commonly caused by direct trauma to the chest, including MVC, pedestrians, and crush injuries. Injuries can range from pericardial injury or cardiac rupture, to mild troponin elevations and sinus tachycardia. Patients at risk for cardiac injury
Treatment GuidelinesEast Trauma Guidelines, 2012 Level 1 Guidelines:
Higher mortality is noted in patients who are hypotensive on presentation, lactate >2.5, co-morbid hemothorax, or elevated troponins. Commotio CordisBlunt force trauma to the pericordium during the t-wave, causing a fine ventricular fibrillation DispositionPatients without other injuries, who are hemodynamically stable with isolated abnormal EKGs or elevated troponins should be admitted for 24-48 hours.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Categories
Archive
February 2018
Please read our Terms of Use.
|
||||||